Metaswitch outbound configuration for ClearIP
ClearIP is a cloud-based solution that complements the Metaswitch CFS with a variety of services, including:
- Analytics
- Telecom fraud prevention
- Robocall and TDoS prevention
- Jurisdictional static and least cost routing
- STIR/SHAKEN caller ID authentication and verification
- CNAM caller ID name information
ClearIP integrates with the Metaswitch CFS using a SIP INVITE—Redirect transaction. SIP messages between the CFS and ClearIP will pass through the Metaswitch Perimeta SBC. The Perimeta will connect to ClearIP over the internet using either a TCP or TLS connection.
This documentation guides you on configuring your Metaswitch CFS and Perimeta to route outbound calls from your network to ClearIP before they are routed to an outbound trunk. These instructions assume you are familiar with using MetaView Explorer.
Here are the configuration steps:
At the end of this page, we’ve provided a complete reference for two Remote Media Gateway models. In all configuration examples, we have highlighted values you should change to match names used in your network.
Configuration process
1. Create a new peering adjacency to your Perimeta SBC
Create an adjacency facing the external ClearIP service on the public internet. There’s nothing unusual about the ClearIP adjacency; just follow the standard Metaswitch documentation.
If you plan to send both outbound and inbound traffic to ClearIP, then ClearIP needs a way to distinguish between outbound and inbound calls. This can be done by setting up two adjacencies: one for outbound calls, and the other for inbound calls. You will need two publicly-addressable IP addresses, one for each adjacency. The adjacency for inbound calls should use a different source IP address than the adjacency for outbound calls.
- Here’s a sample Perimeta adjacency configuration for outbound calls:
adjacency sip ClearIP Outbound adjacency-limits regs 0 regs-rate sustain 0 per-second call-media-policy media-bypass-policy forbid interop ping-enable fail-count 3 interval 10 lifetime 5 listen-transports tcp adjacency-type preset-peering mandated-transport tcp privacy trusted service-address Service Address # service-network 2 # signaling-local-address ipv4 External IP One signaling-local-port 5060 signaling-peer outbound.sip.clearip.com dynamic-routing-domain-match outbound.sip.clearip.com signaling-peer-port 5060 statistics-setting detail default-interop-profile Peer deactivation-mode normal activate
To ensure the Perimeta can resolve ClearIP’s fully-qualified domain name, please check that DNS servers have been configured. This can be done by logging into the Craft Terminal. Select Admin, then Network, then DNS. You will have the option to check the current DNS configuration, set new DNS servers, and test DNS. Please perform a test DNS lookup on sip.clearip.com. If the DNS lookup is successful, you will see a confirmation message like the example below. If the DNS lookup fails, then you will see an error or timeout message and should configure a DNS server.
- Here’s an example of a successful DNS lookup test:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Perimeta ISC LabPerimeta is running This is processor-blade B; processor-blade A is contactable; Session Controller is partnered; processor-blade B is primary [Main->Admin->Network->DNS] [=2 6 4] Manage the DNS server configuration Press ENTER to refresh 0 Back < Back to previous menu 1 Get DNS info Get the current DNS configuration 2 Set DNS servers Set DNS servers 3 Set selection mode Set server selection mode 4 Test DNS Perform a DNS lookup : 4 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Test DNS Perform a DNS lookup to test the configured DNS servers. Enter domain name to query for Default value is: <BLANK> : sip.clearip.com -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Test DNS - Perform a DNS lookup sip.clearip.com Please verify that this command is correct 1 *OK Execute this command 2 Cancel Cancel this operation 3 Modify Modify the parameters of this command : * 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Testing DNS server 8.8.4.4 Looking up sip.clearip.com Using domain server: Name: 8.8.4.4 Address: 8.8.4.4#53 Aliases: sip.clearip.com has address 35.175.114.71 sip.clearip.com has address 35.175.114.72 sip.clearip.com has address 35.175.114.73 sip.clearip.com has address 35.175.114.74 Testing DNS server 8.8.8.8 Looking up sip.clearip.com Using domain server: Name: 8.8.8.8 Address: 8.8.8.8#53 Aliases: sip.clearip.com has address 35.175.114.73 sip.clearip.com has address 35.175.114.74 sip.clearip.com has address 35.175.114.72 sip.clearip.com has address 35.175.114.71 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Result: The command has completed successfully Press ENTER to get list of commands: --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2. Install our Remote Media Gateway model
At the bottom of this page, you’ll find the Remote Media Gateway model that you need to use for this connection. This is the same Remote Media Gateway model used for sending inbound calls to ClearIP.
Copy the text for this model and save it as a text file on your computer with name ClearIPRMGM.txt. Use WinSCP to copy this model text file to your MetaView Server (logging in to WinSCP as defcraft), saving it in the EMSftp directory. If you’re not familiar with using WinSCP, please follow the Metaswitch documentation.
In MetaView Explorer, go to Call Feature Server➔Controlled Networks➔Remote Media Gateway Models.
Find the Import field and enter the name of the file you just uploaded, ClearIPRMGM.txt.
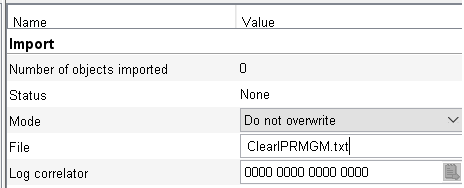
Press Apply, then press the Import button at the bottom of the screen. The new model should be imported.

Check the Status field to see if it was successful. If not, look at the error log.
If you have trouble importing the Remote Media Gateway Model, you can create it manually using the reference output at the end of this page.
3. Create a configured SIP binding for outbound calls
Follow the standard Metaswitch instructions to create a configured SIP binding.
The values should be as follows:
- Set the Contact Domain Name as outbound.sip.clearip.com.
- Set Usage as Trunk.
- Use 5060 as your port, with Contact Address Scheme: Domain name A/AAAA lookup.
- Use the core network IP and port of Perimeta as your proxy IP and port.
- Set Transport Protocol to TCP.
- Select the remote media gateway model you imported above (TransNexus ClearIP).
- Force validation of redirection number: False.
- Perform translations on redirected numbers: False.
- Select new trunk on 3xx response: True.
- Use trunk routing tables to match TG-ID: False.
- Return codes preventing call redirection: 486,600,603,604.
Apply the changes.
- Here’s a sample configured SIP binding configuration for outbound calls:
//UTF8 begin ConfiguredSIPBinding ConfiguredSIPBinding.536872105 // Configured SIP Binding "TransNexus ClearIP Outbound" Name TransNexus ClearIP Outbound Usage Trunk UseDNForIdentification True IPAddressMatchRequired False ContactAddressScheme Domain name A/AAAA lookup ContactIPPort 5060 ContactDomainName outbound.sip.clearip.com SupportedPreferredMediaAddressFamilies Use default SupportedPreferredMediaAddressFamiliesDefaultValue IPv4 SupportedPreferredMediaAddressFamiliesSpecificValue IPv4 SupportedIncomingTrunkGroupParameterType None TrunkGroupParameterTypeOnOutgoingMessages None ProxyAddressScheme IP address and port ProxyIPAddress Perimeta IP Address ProxyIPPort 5060 TransportProtocol TCP MediaGatewayModel ../../MediaGatewayModelContainer/MediaGatewayModel.46 //Remote Media Gateway Model "TransNexus ClearIP" UseMediaIPAddressForNetworkNodeAssignment False NetworkNode Use default NetworkNodeDefaultValue None NetworkNodeSpecificValue None SIPBindingLocation None ESAProtectionDomain None Trusted True UseCallerNameProvidedBySIPDevice True PlayAnnouncementsWhenErrorConditionsOccur False UseStaticNATMapping False MaximumCallAppearances 1024 MaximumConcurrentHighBandwidthCallAppearancesAllowed 0 PollPeerDevice True PollingInterval 30 UseCustomSIPINVITEResponseTimeout False PollCallPaths False ConcurrentNumberOfCallAppearancesInUse 0 ConcurrentNumberOfHighBandwidthCallAppearancesInUse 0 SuppressRedirectionInformation False ForceValidationOfRedirectionNumber False PerformTranslationsOnRedirectedNumbers False SelectNewTrunkOn3xxResponse True UseNormalTrunkRoutingTablesToMatchTgId False ReturnCodesPreventingCallRedirection 486,600,603,604 SignalCallingPartyLATAOnOutboundRequests False DeactivationMode Normal SIPProtocolOptsHeading SIP protocol options SIPProtocolOptsSIPType Basic SIP SIPProtocolOptsDisallowSigForLRN False SIPProtocolOptsAcceptTNSParam False LastCallFailure Last call failure LastCallFailureCause No failure LastCallFailureLogCorrelator 0000 0000 0000 0000 AlarmsHeading Alarms FaultMonitoringProfile None AllowFMPsFromRelatedObjectsToApply True AlarmState Attention Required StatisticsAlarms 0 AlarmLogCorrelator 042e 0721 ac4e b84f AttentionRequiredAlarmEvents 1 AlarmStateTimestamp 1/16/20 3:02:28 PM AlarmResetTimestamp 1/16/20 3:01:32 PM DiagnosticsHeading Diagnostics DiagnosticsLogLevel Default level DiagnosticsAPITraceEnabled False ExportHeading Export StatusHeading Status RequestedStatus Active end //ConfiguredSIPBinding
4. Create a SIP trunk
Follow the standard Metaswitch instructions to create a SIP trunk (under Signaling/SIP/SIP trunks) that uses the configured SIP binding created above for ClearIP.
The following should be configured:
- Select an available Trunk group number.
- Select an available Network number.
- Set Configured SIP Binding to the SIP binding you created for ClearIP above.
- All other fields can be left at the default values.
Apply the changes.
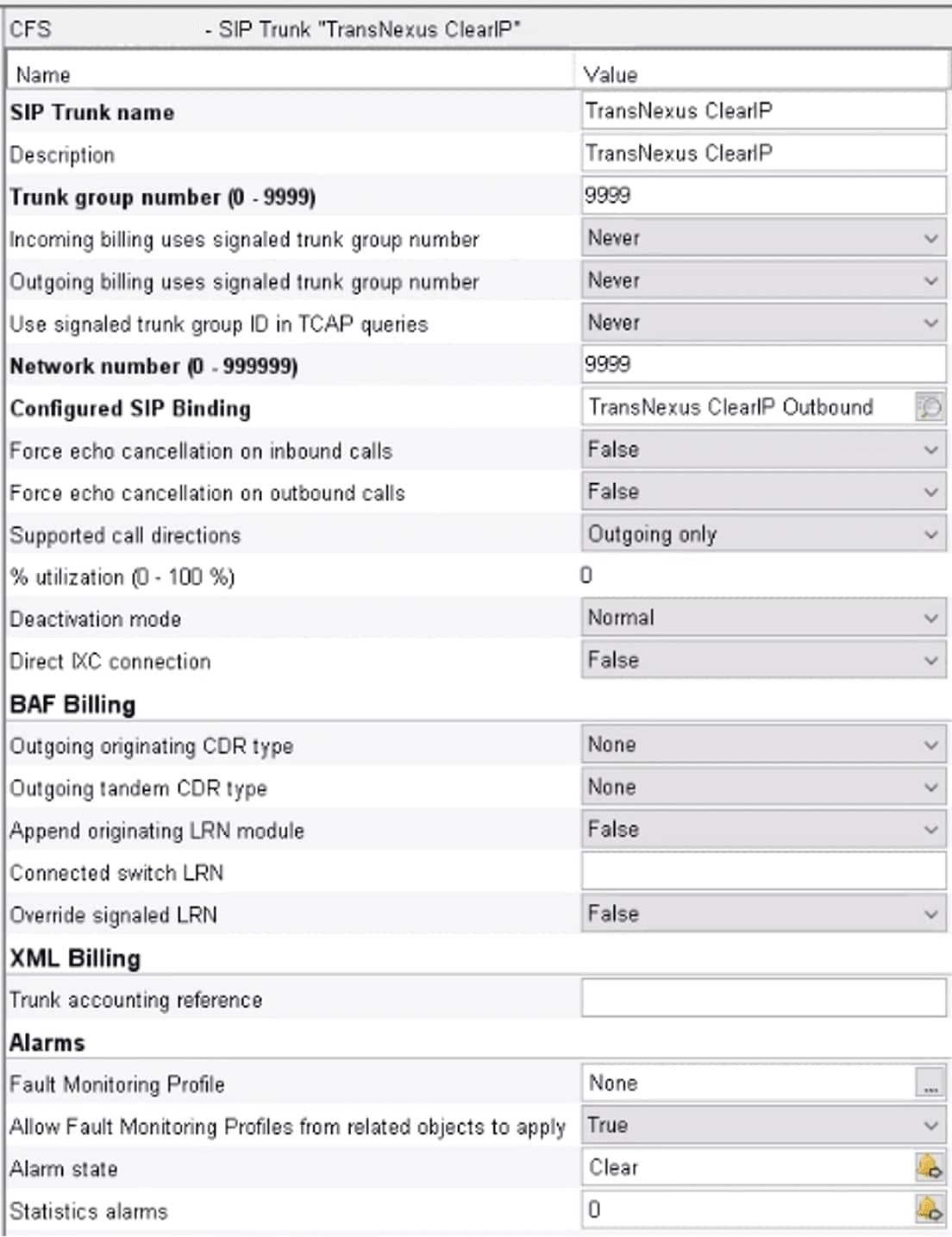
At this point, you’ve built the connection. You have your SIP trunk using a configured SIP binding, optionally routing through the Perimeta over to ClearIP. If you activate this configuration and wait one minute, the binding and the trunk should stay green to indicate that the SIP connection has been established.

5. Update trunk routing
Now that you’ve created the connection, you next need to add it into your trunk routing so that you can use ClearIP.
It is not possible to give step-by-step instructions here, as the details will depend on how your trunk routing tables are configured. Nevertheless, we’ll explain the logic so you can apply the changes to your situation.
First, as with any translations change, make a copy of your active config set, and start editing that copy.
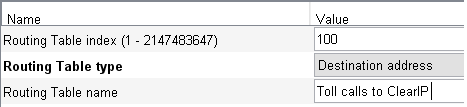
Create a new Trunk Routing table with the following parameters:
- Routing Table type: Destination address
- Routing Table name: Toll calls to ClearIP
- You can use any free Routing Table index
Now create the first Routing Action within that table with the following parameters:
- Description: Send to ClearIP first
- Address type: E.164
- Address scope: Match any
- Wildcard address type: Full wildcard - any type
- Action: Routing complete
- Media channel: ClearIP (found under SIP trunks)
Optional attributes:
- AAR allowed: True
- ARR allowed: True
You now need to decide where to place this new table in your trunk routing logic.
In a typical least cost routing application, you’ll want to route all toll calls to this SIP trunk and rely on ClearIP to return the trunk group numbers to use for each call. If ClearIP is unable to route the call for some reason, then your existing trunk routing tables will be used as backup.
If you’re using CleariP for telecom fraud detection, then you’ll want to route all toll calls to this SIP trunk. The behavior will be slightly different. If ClearIP detects fraud, then it can return a SIP 603 Decline so the call is blocked. With normal calls, ClearIP will return a SIP 404 Not Found, which will cause the Metaswitch to overflow to your standard trunk routing logic.
In either case, you’re looking for the place in your trunk routing tables where you first split off toll calls. Often your routing will start by identifying operator and 911 calls. Then perhaps you’ll have a table that identifies toll calls versus local calls. Assuming you find this place, here’s what you need to do:
- Find the routing action that matches on toll calls and take a note of the next table parameter. Let’s say the next table is table N.
- Modify this routing action so the next table is set to your new table, Toll calls to ClearIP.
- Create a second routing action under the Toll calls to ClearIP table with the following parameters:
- Address type: E.164
- Address scope: Match any
- Wildcard address type: Full wildcard - any type
- Action: Table lookup
- Next table: Routing table N
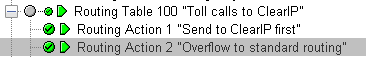
As you look at the logic, you’ll see that now all toll calls route through the ClearIP table and are routed over the ClearIP SIP trunk first.
If ClearIP identifies telecom fraud, it will return a SIP 603 Decline to reject the call. If it ClearIP can route the call, it will send back a SIP 302 Moved Temporarily identifying which trunk to use. Otherwise, for normal calls, ClearIP will return a SIP 404 Not Found and the call will pass back into your existing routing logic (table N).
In some routing schemes, international calls may be split out separately from national long distance calls, in which case you’ll also want to route them to ClearIP. The simplest way to handle this is to create a duplicate Routing Table to send international calls to ClearIP, duplicating all the above logic but for international calls.
Caution: We recommend that you do not send outbound calls made to Public Safety Answering Points (PSAPs), for example, 911 calls, to ClearIP. If ClearIP configurations are not made carefully to account for emergency calls to PSAPs, then these critical calls could be inadvertently blocked.
Instead, we recommend that you configure your Metaswitch translation tables to route such calls directly to the PSAP. Consult the Metaswitch documentation for further instructions.
6. Testing
Once you’ve built all this configuration, you’ll want to test the solution before deploying to your entire network. In order to do this, we recommend setting up a test line and using the Overriding config set parameter on that line to use the new config set for all calls from that test line, without activating the new config set globally on the switch.
Once you’ve done that, you should work with the TransNexus team to perform some basic tests and then figure out the best plan to roll out the solution more widely to your subscribers.
A note about SIP response codes
When ClearIP rejects a call for suspected fraud, it returns a SIP 603 Decline response, indicating that the call has failed and should not be retried. The configuration described above prevents the Metaswitch from attempting to re-route these rejected calls to an overflow trunk and will set the internal Q.850 code used to track the call failure to be 21, which means call rejected.
However, if this call originally arrived at your Metaswitch over a SIP trunk (perhaps your Metaswitch is tandeming the call or it was placed from a SIP PBX) then be aware that by default the Metaswitch will send a SIP 486 Busy Here to the SIP caller (it doesn’t use the same 603 response code).
In general this is fine, but if you wish to replace that error response with something different (e.g. a 603) you can do so by modifying the Remote Media Gateway Model(s) associated with the relevant inbound Configured SIP Bindings (e.g. your network SIP trunk or SIP PBX).
On each Remote Media Gateway Model, you can explicitly request the Metaswitch to send a 603 response when using a Q.850 code of 21. To do this, find the parameter Q.850 cause code to SIP response code mapping table, and add a new line that says: 21,603
Reference: Remote Media Gateway models
- Remote gateway model for MetaView Server version 9.5.30 or higher
//UTF8 begin MediaGatewayModel // Remote Media Gateway Model “TransNexus ClearIP” Category SIP ModelName TransNexus ClearIP Description TransNexus ClearIP ControlProtocol SIP DefaultModel False AlertInfoStringsForDistinctiveRingingHeading Alert-Info strings for Distinctive Ringing NumberFormatsHeading Number formats NumberFormatsCalledNumberFormatInternationalScope NF<INT> NumberFormatsCalledNumberFormatNationalScope NF<INT> NumberFormatsCallingNumberFormatInternationalScope NF<INT> NumberFormatsCallingNumberFormatNationalScope NF<INT> NumberFormatsRedirectNumberFormatInternationalScope NF<INT> NumberFormatsRedirectNumberFormatNationalScope NF<INT> NumberFormatsOverrideAutogeneratedCallerID False SignalingSettingsHeading Signaling settings SupportedHighBandwidthMediaFormats {G.711 u-law} LowBandwidthVoiceCodecsSupportedAsStandard {} SupportedDataCodecs {} AdvancedVoiceCodecsPermitted No VideoCodecsPermitted No MaximumNumberOfVoiceCodecsSupported 5 PacketizationInterval 20 SilenceSuppressionAllowed False MaximumSimultaneousTransactionsOutstanding 300 DigitOverhangTime 250 OverrideToHeaderUserPartOnINVITEs False FixBitsMGCPMeGaCoSIPMSML {Cannot be hub,Simple contexts,No loopback between contexts,Restricted direct media,Cannot play ringback,Cannot control endpoint connectivity,Connections always receive,Cannot report detection of call-type discrimination tones} DynamicFixBitsMGCPMeGaCoSIPMSML {} FixBitsSIP {Include transport parameter in From header,May loop calls back to MetaSwitch,Trust number portability information (npdi),Supports receiving number portability information (npdi),Supports receiving carrier information (cic=XXXX)} FixBitsSIP2 {Supports GETS Resource-Priority header} FixBitsSIP3 {Use calling name from P-Asserted-Identity (if present)} FixBitsSIP4 {} FixBitsSIP5 {} SIPResponseCodeToQ850CauseCodeMappingTable 603,21 SIPResponseCodeForESAFailure 503 SIPResponseCodeForCongestion 500 RingLengthForUseWithICF 4 SupportsNotifysRequestingResynchronization False ReferenceCount 1 UpToDateCount 1 ParameterNamesForLineClassCodeHeading Parameter names for Line Class Code ExportHeading Export StatusHeading Status RequestedStatus Enabled end //MediaGatewayModel - Remote gateway model for MetaView Server versions older than 9.5.30
//UTF8 begin MediaGatewayModel // Remote Media Gateway Model “TransNexus ClearIP” Category SIP ModelName TransNexus ClearIP Description TransNexus ClearIP ControlProtocol SIP DefaultModel False AlertInfoStringsForDistinctiveRingingHeading Alert-Info strings for Distinctive Ringing NumberFormatsHeading Number formats NumberFormatsOverrideAutogeneratedCallerID False SignalingSettingsHeading Signaling settings SupportedHighBandwidthMediaFormats {G.711 u-law} LowBandwidthVoiceCodecsSupportedAsStandard {} SupportedDataCodecs {} AdvancedVoiceCodecsPermitted No VideoCodecsPermitted No MaximumNumberOfVoiceCodecsSupported 5 PacketizationInterval 20 SilenceSuppressionAllowed False MaximumSimultaneousTransactionsOutstanding 300 DigitOverhangTime 250 OverrideToHeaderUserPartOnINVITEs False FixBitsMGCPMeGaCoSIPMSML {Cannot be hub,Simple contexts,No loopback between contexts,Restricted direct media,Cannot play ringback,Cannot control endpoint connectivity,Connections always receive,Cannot report detection of call-type discrimination tones} DynamicFixBitsMGCPMeGaCoSIPMSML {} FixBitsSIP {Use E164 numbers,Include transport parameter in From header,May loop calls back to MetaSwitch,Trust number portability information (npdi),Supports receiving number portability information (npdi),Supports receiving carrier information (cic=XXXX)} FixBitsSIP2 {Supports GETS Resource-Priority header} FixBitsSIP3 {} FixBitsSIP4 {} SIPResponseCodeToQ850CauseCodeMappingTable 603,21 SIPResponseCodeForESAFailure 503 SIPResponseCodeForCongestion 500 ParameterNamesForLineClassCodeHeading Parameter names for Line Class Code ExportHeading Export StatusHeading Status RequestedStatus Enabled end //MediaGatewayModel